In today’s digital age, the online presence of any business plays a crucial role in its success. That’s where Search Engine Optimization comes into play.
In this comprehensive SEO for Beginners guide, I will walk you through the basics of SEO. By the end of this article, I’m sure you will be able to navigate the world of SEO and propel your online presence to new heights.
What is SEO?
SEO, which stands for Search Engine Optimization the practice of optimizing your website and its content to rank higher in search engine results. It is the backbone of digital marketing and online success. When users search for anything, SEO ensures that your website appears prominently, making it more likely for users to click on your link and visit your site.
Most people think creating backlinks or optimizing content around a keyword is SEO. But believe me, it’s not. I have been in the industry for the past 8 years and whenever I read a new Google update, I find something that changes the previous knowledge.
The fundamental are still the same but other things have changed that you will learn soon. Now let’s start with all the details you need to know about search engine optimization.
Why SEO Is Important?
I’m going to tell you the importance of SEO in simple words.
So as you can see I have googled “best affordable gaming laptop” and it’s showing 37,800,000 results. Accoring to research, there are more than 500 million Google searches per hour. But how many of them visit second page of Google?
Moz conducted a study and found that Over 90% of people never click on the second page of Google search results. Yes, you read that right. Most users simply do not go beyond the first page of search results. Now, here comes the crucial question: Where does your website rank?
It’s buried on the second page or beyond. The chances of people discovering it are almost non-existent. Your carefully curated content might as well remain hidden from the very audience you intended to help. That’s where SEO will help you.
If you write well-researched content and create some quality backlinks, there is a chance that you can significantly improve your website’s rankings and increase its visibility to potential customers.
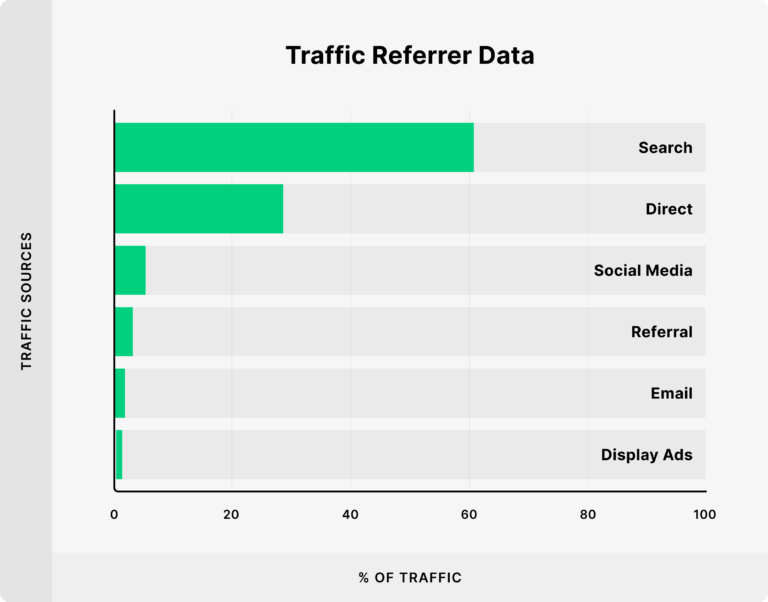
One more thing is that over 60% of all traffic on the internet comes from search engines. Which is also know as organic traffic.
White Hat SEO vs. Black Hat SEO
There are two primary approaches to SEO.
- White hat SEO involves using ethical and legitimate practices per Google guidelines to optimize your website and earn search engine rankings.
- On the other hand, black hat SEO employs unethical tactics that violate search engine guidelines, risking penalties and potential removal from search results.
As a beginner, it’s essential to focus on white hat SEO methods to build a sustainable online presence.
SEO in a Nutshell
There are four main types of SEO that I will discuss in detail below.
- On Page SEO
- Off-Page SEO
- Technical SEO
- Local SEO
SEO may initially seem overwhelming, but it will be easy once you understand its basics. I’m telling you this because of my experience. I have trained many students, so I know how it feels when you start learning it, but don’t worry, I will give my best.
Related: Best Startup Marketing Strategies
What Are Search Engines?
Search engines are web-based tools that allow you to enter keywords or phrases and provide results based on your search query. They enable users to find information quickly and effectively online, drawing from various sources. SE are essential components of our online lives, from news searches to purchasing products, they are everywhere!
They have been around since 1990, with the first major being Archie created by Alan Emtage at McGill University in Montreal, Canada. The most well-known search engine is Google, which was founded in 1998. In addition to Google there are many other popular search engines such as Yahoo!, Bing, DuckDuckGo, and Baidu.
Search engines use bots, also known as crawlers or spiders, to discover and index web pages. These bots systematically crawl through websites, analyzing their content and links.
How Search Engines Work?
To comprehend SEO fully, you must understand how search engines deliver results to users. The process basically depends on three essential steps:
- Crawling: As mentioned, crawling involves search engine bots exploring websites and gathering information about their content and structure.
- Indexing: Once a website is crawled, its information is stored in a massive database of web pages in the search engine’s index.
- Ranking: When a user performs a search, the search engine’s algorithm ranks web pages based on their relevance and authority.
When it comes to your site ranking, there are a lot of factors that influence it. It’s not just about content and backlinks anymore.
Now if you see the crawling step is very important. If SE spiders did not crawl your site, it would not get indexed. No indexing means no ranking.
Why Follow Google Search Engine Guidelines?
Google is one of the biggest search engines in the market and owns 92.64% of the market. 95% of the visitors on the internet use Google instead of other search engines when searching for something. Other platforms like Bing and Yahoo have the same SEO guidelines as Google. So that’s why most people follow Google instead of others.
Organic vs. Paid Search Results
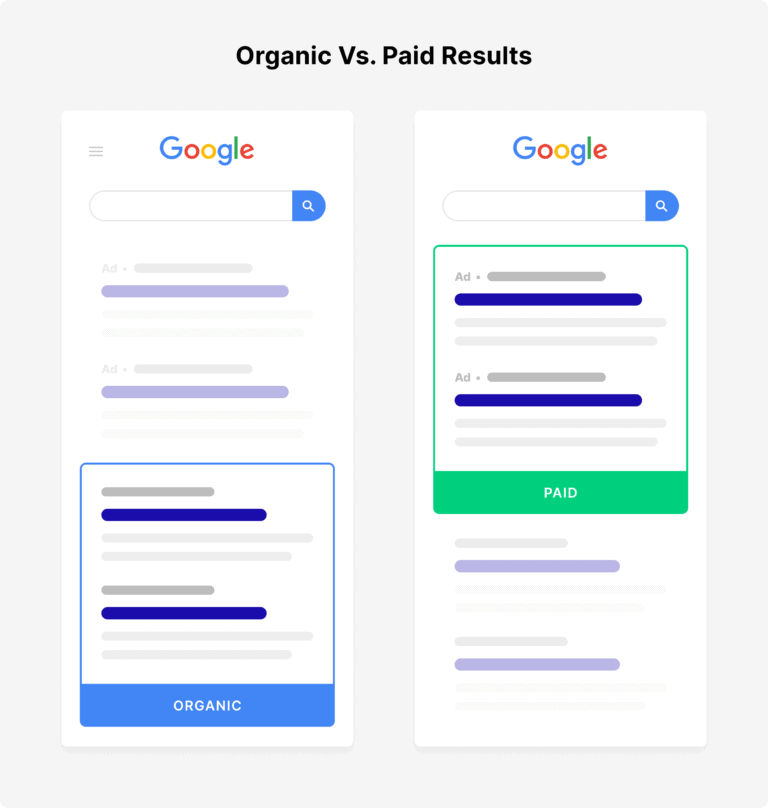
When you search for something on Google, you might have noticed that the results can be categorized into two types: organic and paid. Understanding the difference between these two is crucial. Both of them are effective and have some pros and cons. I would say it depends on your goal. Let’s understand both of them.
Organic Search Results:
Organic results are the unpaid listings displayed on the search engine results page (SERP). They are ranked based on relevance and quality, as determined by the search engine algorithm.
Key Characteristics of Organic Search Results:
- Free Traffic: One of the significant advantages of organic search results is that you don’t pay the search engine to appear in these listings. Instead, your website’s ranking is based on its relevance and authority concerning the search query.
- Trust and Credibility: Users trust organic search results more than paid advertisements. They believe that websites appearing organically have valuable and reliable content related to their search.
- Long-Term Sustainability: While improving your organic rankings may take time and effort, the results are often more sustainable in the long run. Once your website gains authority and relevance, it can remain in search results without continuous payments.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): Organic listings receive more clicks than paid ads. Users often skip over paid results and focus on the organic listings that match their search intent.
Paid Search Results
Paid results, also known as pay-per-click (PPC) ads, are sponsored listings that appear on top or bottom of the SERP. Advertisers bid on keywords, displaying their ads when users search for those keywords.
Key Characteristics of Paid Search Results:
- Immediate Visibility: Unlike organic rankings that require time and SEO efforts to improve, paid search results offer instant visibility for your website. Once you create and set up your ad campaign, your website can appear on the first page of search results.
- Targeted Reach: PPC ads allow you to target specific keywords, demographics, locations, and user behavior. This level of targeting enables you to reach your desired audience more precisely.
- Flexibility and Control: With paid ads, you control your ad budget, copy, and campaign duration. This flexibility allows you to adjust your strategy based on performance and budget constraints.
- Performance Measurement: PPC platforms provide detailed analytics and performance metrics, enabling you to measure the success of your ad campaigns and optimize them for better results.
Both organic and paid search results have their merits, and the best approach for your business depends on your goals, budget, and target audience. But personally I’m not a big fan of PPC ads because SEO has many benefits compared to paid ads.
Understand Customers and Keywords
Understanding your customers and the keywords they use is important for success. Keywords act as a bridge between what your potential customers are searching for and the content you provide on your website. But before doing keyword research, ask the following questions from yourself to understand your audience better.
- What is the primary goal of my website or business?
- Who is my target audience?
- What products, services, or content do I want to promote?
- What are the main topics or themes of my website?
- Who are my competitors?
- What are the current keyword rankings for my website?
- What are the popular industry-related terms and jargon?
- Are there any seasonal or trending keywords relevant to my
- What are the long-tail keywords related to my primary topics?
- What tools and resources can I use for keyword research?
You can gain valuable insights into your target audience’s search behavior and preferences by answering these FAQs.
Remember that understanding your audience is an ongoing process, and regularly revisiting these questions can help you stay in touch with their evolving needs and optimize your content accordingly.
What is Search Intent?
Search intent, also known as user intent, is a term used to describe the purpose of why someone has typed a particular query into a search engine. It is important in optimizing websites for organic traffic and ensuring users find what they want in their search results. Let’s break keyword types with examples to ensure you fully understand this concept.
Types of Keywords
The purpose of every search is different. Some are trying to find information while others are looking for something to buy. To understand the intent behind the keyword, you need to know its type.
Short-Tail Keywords also known as head or broad keywords, are short phrases, usually one to three words long.
Examples: “shoes,” “digital marketing,” and “travel destinations.”
Long-Tail Keywords are longer and more specific phrases, typically containing four or more words. They are more targeted and have lower competition.
Examples: “Women’s running shoes for flat feet,” or “Digital marketing strategies for small businesses”
Geo-Targeted Keywords include location-specific terms targeting a specific city, region, or country. These keywords are valuable for local businesses and services.
Examples: “plumber in Los Angeles” or “digital marketing agency in Sydney.”
Branded Keywords include the name of a specific brand, company, or product. They are used by users specifically searching for a particular brand or its offerings.
Examples: “Nike shoes,” “Apple iPhone,” “Coca-Cola.”
Product Keywords refer to specific items or models of products. These keywords are commonly used by users who are ready to make a purchase.
Examples: “iPhone 12 Pro Max 256GB,” “Sony 4K Smart TV,” “Canon EOS Rebel T7i.”
Informational Keywords are used by users seeking information or answers to their questions. They are often used in research or learning contexts.
Examples: “how to tie a tie,” “benefits of yoga,” and “history of the Eiffel Tower.”
Transactional Keywords indicate that the user is ready to make a transaction or take a specific action, such as signing up for a service or purchasing.
Example: “Subscribe to Netflix,” “Get a quote for auto insurance.”
Commercial Investigation Keywords are used by users in the buying process’s consideration stage. Before deciding, they are looking for comparisons, reviews, or more in-depth information about products or services.
Examples: “Best laptops for students 2023,” “Review of XYZ web hosting,” and “Top-rated digital cameras.”
Navigational Keywords are used by users looking for a specific website or webpage. They already know what they want and use search engines to find the direct link.
Example: “Facebook login,” “YouTube,” “Amazon Prime.”
Understanding the different types of keywords and their intent can help you target the right audience and improve your website’s visibility and search engine rankings.
Keyword Research Tools
There are many tools out there that can help you find the right keyword and its intent. Having the right tools can make the process more efficient and effective. Here are some of the most popular keyword research tools that beginners can use:
- Google Keyword Planner: This tool by Google provides you with keyword ideas and traffic estimations, helping you understand how a list of keywords might perform. It can also give you a sense of the competition level for each keyword.
- SEMrush: SEMrush is an all-in-one SEO tool with robust keyword research features. It provides data on keyword volume, keyword difficulty, and competitive density. SEMrush also allows you to analyze your competitors’ SEO strategies.
- Ahrefs Keywords Explorer: Ahrefs provides extensive keyword data, including search volume, keyword difficulty, and how many clicks you can expect from a particular keyword. It’s my favorite.
- Ubersuggest: A free tool by Neil Patel, Ubersuggest provides keyword suggestions, search volume, and competition level. It also reveals the top-ranking pages for each keyword.
- Answer The Public: This is the right tool if you want everything on a keyword. I can show you the most relevant keywords and all the FAQs around that per your query. I would highly recommend you check it out.
Remember, these tools are just a starting point. They can help you identify potential keywords, but it’s up to you to analyze that data and decide which keywords are the most relevant and valuable for your website.
Content Creation in SEO
Content marketing is a fundamental aspect of SEO and is crucial in driving organic traffic to your website. In SEO, content refers to any information on your website, including text, images, videos, infographics, and more. Writing content and using keywords in it is not enough. Google makes a lot of changes in its search algorithm and now you have to take care of EEAT.
E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) is part of Google’s Search Quality Rater Guidelines—the handbook that real people use to evaluate the quality of search results.
E-E-A-T is important for several reasons.
First, it enhances the credibility of your content. When your content demonstrates high levels of expertise, authority, and trustworthiness, it inspires confidence in your audience. It leads to improved engagement, more shares, and the potential for higher quality backlinks.
Second, Google’s algorithms are designed to prioritize high-quality content that provides value to users. Websites consistently producing content with high E-E-A-T will likely rank better in search engine results.
To optimize your content for it:
- Ensure that qualified individuals write it or are thoroughly researched and accurate.
- Include clear author biographies and credentials to demonstrate expertise.
- Make sure your content is well-referenced, citing reliable sources to demonstrate authority.
What is High-Quality Content?
The term “High-quality content” is frequently used in digital marketing; however, its definition can be elusive. High-quality content is substantive, well-researched, and provides significant value to its intended audience.
This kind of content usually goes beyond the surface of a topic to offer in-depth, actionable information. It’s not just about delivering facts, it’s about providing context, insights, and practical tips that readers can apply in their situations.
It often has a strong narrative element, guiding the reader through the information in a clear, coherent, and engaging way. From a structural perspective, it’s well-organized, utilizing headings, subheadings, bullet points, and other formatting tools to make the content readable and scannable.
Things In Quality Content
- Value: Provide valuable and relevant information to your audience.
- Readability: Use clear and concise language that is easy to understand.
- Originality: Avoid duplicate content and plagiarism.
- Formatting: Organize your content with headings, bullet points, and images for better readability.
- Engagement: Encourage reader engagement through calls-to-action and questions.
Types of Content
Let’s look at the various types that can be created:
- Blog Posts: Blogging is an excellent way to regularly update your website with fresh content and keywords and provide valuable information to your audience. They’re also great for promoting engagement and creating an online community.
- Articles: Similar to blog posts, articles allow you to provide in-depth information on a particular topic, cover industry news, or produce a piece of investigative journalism.
- Videos: Search engines increasingly prioritize video content. Videos can be an excellent way to keep visitors on your page for longer, improving dwell time and positively impacting your website’s SEO.
- Infographics: Visual representation of data or information can engage the audience. They are a great way to present complex information in an easy-to-understand format. They’re highly shareable, which can increase visibility and backlinks to your website.
- How-To Guides or Tutorials: This content is an excellent way to provide users with practical knowledge. It can often capture high-quality, targeted traffic, which improves your site’s authority and relevance.
- Lists: A list (like this one) is an article that provides information in a number list format. They’re easy to scan and are often highly shareable, helping you earn backlinks and improve your SEO.
- Glossaries: If you work in a niche industry, creating a glossary of terms can be a particularly effective way to capture SEO traffic.
- Directories or Resource Pages: These pages provide a consolidated list of links or resources for a specific topic. They can be a strong magnet for backlinks, enhancing your website’s SEO.
On Page SEO
On-Page SEO refers to the practice of optimizing individual web pages. It involves both the content of the page and the HTML source code.
Following are a few components of on-page SEO that you should understand.
Content Optimization
Content is the heart of your website and a critical factor. Optimization involves strategically incorporating relevant keywords in your content, including title tags, meta descriptions, and body content. Plus you can also add LSI keywords.
Internal Linking
Creating a map of links of your site can help Google bot crawl entire site, it’s called Internal linking. It is a powerful SEO technique that involves linking one page of your website to another page on your website.
This practice helps improve your site’s navigability, distributes page authority and ranking power throughout the site, and enhances the user experience by providing them with additional reading options.
Mobile-Friendliness
As more and more people use their smartphones to access the internet, mobile-friendliness has become a critical factor in SEO. A mobile-friendly website is designed to work the same way across all devices.
This means that nothing changes or looks unusual when users switch from their desktop to their mobile device. Google has also shifted towards mobile-first indexing, which means it predominantly uses the mobile version of the content for indexing and ranking.
Image Alt Texts
Alt text, or “alternative text,” is an HTML attribute applied to image tags to provide a text alternative for search engines. Applying images to alt text such as product photos can positively impact an ecommerce store’s search engine rankings.
Page Speed
Page speed is a critical factor in SEO. It refers to the time it takes for the content on your website’s page to fully load. A slow-loading page can be a significant detriment in a fast-paced world where users expect instantaneous results.
Slow page speeds lead to higher bounce rates as users are unlikely to wait for your page to load. Google also considers page speed in its ranking algorithm, with faster pages receiving a ranking boost.
Mastering these basic components of on-page SEO will help ensure your website performs well in SE rankings and provides a quality user experience.
Off-Page SEO aka Link Building
Off-Page SEO refers to actions taken outside of your website to impact your rankings within search engine results pages (SERPs). It primarily involves improving the perception of a site’s popularity, relevance, trustworthiness, and authority. Now, let’s discuss some key elements.
What is a Backlink?
Backlinks, also known as inbound or incoming links, are links from one website to a page on another website. They are considered “votes” for specific pages, indicating that the content is credible, and useful to search engines. In other words, when a reputable website links to your content, it signals to search engines that it is valuable and relevant. However, not all backlinks are created equal.
Types of Links:
In the world of backlinks, several links can be categorized based on their attributes and relevance.
- Natural Links: These are organic links that other websites create voluntarily without manipulation. These links typically occur when your content is so valuable or informative that others find it worth referencing or sharing.
- Manual Links: Also known as editorial links, manual links are backlinks acquired through intentional efforts like outreach and guest posting. These links are obtained by building relationships with other website owners or editors.
- Self-Created Links: These links are created through user-generated content platforms, forum signatures, or blog comments. However, search engines often devalue such links as they may not reflect genuine endorsements.
I’m not a big fan of link building but it’s still an important aspect of SEO which can change the game.
Dofollow vs. Nofollow Links
When we acquire or create a backlink from any website, we receive an attribute. Most SEO experts will say these are the types of backlinks, but I don’t see it that way. Dofollow and nofollow are link attributes that tell search engines how to treat a particular link.
- Dofollow links are standard hyperlinks that pass link equity from the referring website to the linked page. They signal to search engines that the referring website endorses the linked page and should be considered for ranking.
- Nofollow links, as the name suggests, instruct search engines not to pass link equity to the linked page. These links are often used when a website wants to link to a page without giving it SEO credit or authority. These links are commonly found in user-generated content and paid advertisements.
Top Link Building Strategies:
- Guest Posting: Writing high-quality guest posts for reputable websites in your industry is an excellent way to build backlinks. Ensure that the content you provide is valuable, informative, and relevant to the audience of the target website.
- Broken Link Building: Identify broken links on other websites, and reach out to the website owners, suggesting your content as a replacement. This tactic helps them fix broken links while earning a backlink for your website.
- Influencer Outreach: Collaborate with influencers and authoritative figures in your niche to co-create content or obtain mentions and backlinks from their websites or social media platforms.
- Content Marketing and Promotion: Create valuable and shareable content, such as infographics, videos, or comprehensive guides, and promote them across social media and relevant online communities to attract natural backlinks.
- Participate in Online Communities: Engage in industry-specific forums, discussion boards, and social media groups, establishing yourself as an expert and sharing relevant content when appropriate.
- Link Reclamation: Identify mentions of your brand or website without backlinks, and reach out to the website owners, requesting them to turn them into clickable backlinks.
- Collaborate on Round-Up Posts: Contribute to expert round-up posts organized by other websites in your industry. Multiple experts share their insights on a specific topic in these posts, and you get a backlink in return.
There are a lot of other things that go into off-page SEO, but these basic things can help you understand the concept.
Intro to Technical SEO
Most digital marketers often overlook an essential aspect of SEO: Technical SEO. It refers to the backend optimizations of your website that help search engine spiders crawl and index your site more effectively. The primary aim is to improve your site’s infrastructure.
It lays the foundation for your website’s visibility on search engines. Without a technically sound website, your top-quality content and robust backlink profile may go unnoticed by search engines.
Many ignore this aspect of SEO because it can be complex and daunting, especially for beginners. But you don’t have to be afraid. It’s not rocket science. Following are a few things you should know about it.
Check Your Robot.txt Files
The robots.txt file is like a roadmap for search engine bots, guiding them on which pages to crawl and index and which to avoid. This file controls how search engines access and interact with your website’s content. By correctly setting it up, you can prevent search engines from indexing certain pages, like duplicate content or sensitive information, which might negatively affect your SEO efforts.
CSS, JavaScript
Search engines rely on CSS and JavaScript to understand your website’s structure, layout, and user interactivity. Ensuring that search engine bots can access and render these elements properly is essential. If search engines encounter issues with CSS and JavaScript, they may not fully understand your website’s content and user experience, resulting in lower rankings.
Setup HTTPS
Website security is paramount for protecting your users and SEO purposes. HTTPS is a secure communication protocol that encrypts data transmitted between your website and visitors. Search engines, especially Google, consider HTTPS as a ranking signal. Websites with SSL certificates (HTTPS) rank higher in search results, making it a vital aspect of technical SEO.
Mobile SEO
With the rapid increase in mobile internet usage, mobile SEO has become critical in ranking higher in search results. Mobile-friendly websites are more likely to provide a positive user experience, leading to better engagement and higher rankings. Ensure your website is responsive, adjusts to different screen sizes, and provides seamless navigation on mobile devices.
Page Speed
Your website speed is an essential aspect that directly influences user experience and search engine rankings. Slow-loading pages can lead to high bounce rates and decreased user satisfaction, negatively impacting your SEO efforts. Optimize your website’s performance by compressing images, minimizing code, and leveraging browser caching to improve page speed.
Structured Data Markup
Also known as schema markup, it is a way to provide additional information to search engines about the content on your website. By adding schema markup to your web pages, you help search engines better understand the context of your content, which can lead to enhanced search results in the form of rich snippets and featured snippets.
Canonical URLs
Canonical URLs are essential when you have multiple versions of the same content on your website. For example, suppose you have a print-friendly version and a regular version of a page. In that case, you should use a canonical tag to indicate the preferred version to search engines. This prevents duplicate content issues and ensures that search engines direct their ranking signals to the correct page.
XML Sitemap
An XML sitemap is a list of all the pages on your website designed to help search engine crawlers navigate and understand your website’s structure. Including an XML sitemap in your website’s root directory makes it easier for search engines to discover and index your content. You can use tools like Yoast SEO and Rank Math for this.
Mobile-First Indexing
Google has adopted mobile-first indexing, meaning it primarily uses the mobile version of a website for ranking and indexing purposes. As a result, having a mobile-friendly and responsive website is crucial to maintaining and improving your search engine rankings.
Website Architecture
A well-organized website architecture is essential for both users and search engines. Create a clear hierarchy of pages with a logical and intuitive navigation structure. This helps users find the information they need and allows search engines to crawl and index your website more efficiently.
Technical SEO serves as the backbone of your website. These foundational elements will enhance your website’s overall performance and visibility, increasing organic traffic and improving search engine rankings.
How To Track & Measure SEO Results?
Last but not least, measuring the success of your SEO efforts is a critical step. Google Analytics and Search Console can help you with this. Following are some metrics to consider when evaluating your SEO performance.
1. Google Analytics provides valuable insights into your website’s traffic, user behavior, and conversions. Some key metrics to monitor include:
- Organic Traffic: Analyze the number of visitors visiting your site through organic search. Observe the trends and look for improvements over time.
- Bounce Rate: A high bounce rate could indicate that your content is not meeting user expectations or that your website’s user experience needs improvement.
- Time on Page: Measure how much time users spend on your pages. Longer time on the page suggests engaging content.
- Conversion Rate: Track the percentage of visitors who complete desired actions, such as purchasing or signing up for a newsletter.
2. Google Search Console provides data on how Google crawls and indexes your site. It offers valuable insights into your site’s search performance. Key metrics to focus on include:
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): Measure the percentage of users who click on your site’s link when it appears in search results.
- Impressions: Track the number of times your website appears in search results.
- Average Position: Monitor the average ranking position of your site for specific keywords.
SEO is an ongoing process that takes time to see significant results. Continuously monitor and analyze your SEO metrics, adjust your strategies accordingly, and stay up-to-date with industry trends.
Final Thoughts
Mastering SEO for beginners involves understanding the basic concept of each point. If you don’t know the starting point, how will you do it on the advanced level? So that’s it for now. I’m sure this guide for SEO for beginners would help you understand the concept before diving into other things. If you have any questions or do not understand anything, just let me know in the comments.